Test coverage guide
How to divide test granularity
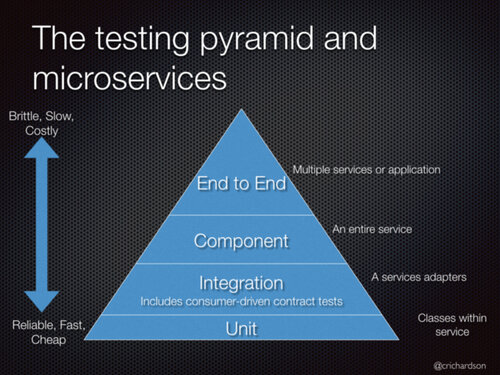
How to divide test granularity is a big problem. Chris Richardson has divided unit test, integration test, component test and end-to-end test for services test in "Descending the Testing Pyramid: Effective Testing Strategies for Microservices". We can use it for reference in the process of designing test cases.
Unit Test
1.The benefits of unit testing
- Unit test code can help everyone to go into details and understand the function of the code.
- We can find bugs by test case, and then enhance the robustness of the code.
- Test case code is also the demo usage of the core code.
2.Some design principle of unit test case
- Steps, fine-grained and combination conditions should be well designed.
- Attention to boundary condition test
- Test code should also be designed without writing useless code.
- When you find a
methodthat is hard to write unit test, if you can be sure themethodis "smelly code", then refactor it with the committer. - The mock framework in seata is: mockito. Some tutorials:mockito tutorial,mockito refcard
- TDD(optional):When you start a new issue, you can try to write test case at first
3.The specified value of the test coverage
- In the stage, the test coverage specified value of delta changed codes is :>=80%. The higher, the better.
- We can see the coverage report in this page: https://codecov.io/gh/apache/incubator-seata
4.Project agreement
- The unit test cases of the Seata project are distributed in each sub module of the project, and the test assertion class ends with Test.
Integration test
Project agreement
- Integration test in this project generally refers to the test above unit test level.
- This project use github actions、jiblib maven plugin、fabric maven plugin、testContainers to build Docker images,and build integration test environment
- Different from unit test, if a test case needs to rely on the third-party middleware, you can use the above tools to build the docker environment and test without mock. But also pay attention to the granularity of building components. For an overly complex environment, you can: the middleware on which the core test depends can be built by docker, and the middleware on which the core test depends can be mocked
- The integration test cases of the Seata project are uniformly placed in the integration-test sub module, and the test assertion class ends with IT.
- Junit5 is used here
- In the process of parallel running of test cases, pay attention to the isolation state of common middleware, plan the test data and prevent conflicts.