Background
In distributed transactions, we often encounter scenarios where messages need to be sent, such as notifying the inventory service to reduce inventory after an order is successfully paid. But how to ensure the consistency between local transactions and message sending? This requires using a distributed transaction solution to solve this problem. Seata, as an open-source distributed transaction solution, provides support for RocketMQ, making it easy to send messages in distributed transactions.
Solution Design
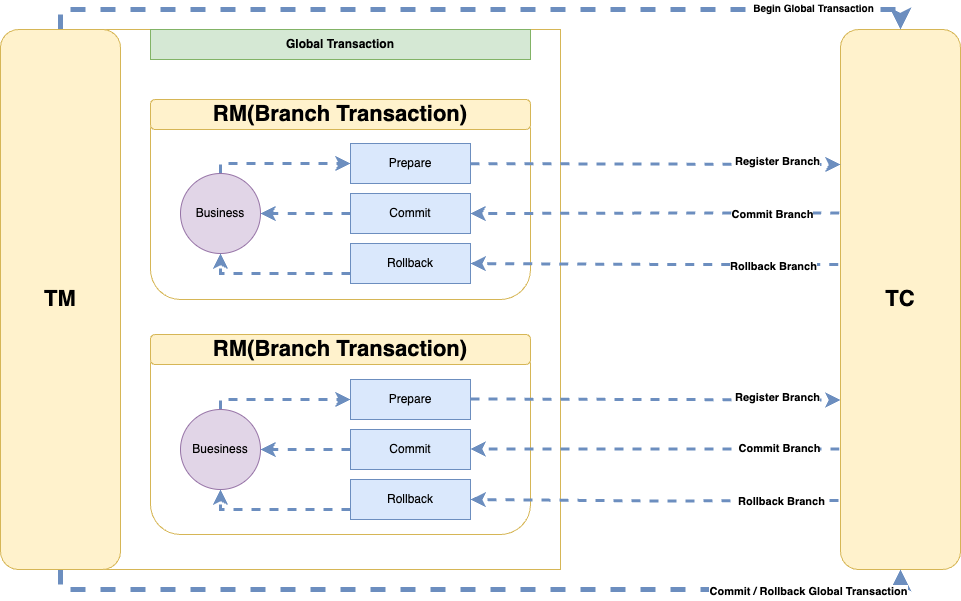
Let's first review the overall process of TCC through the above diagram:
- The Transaction Manager (TM) initiates a global transaction.
- The Resource Manager (RM) tries to execute the prepare method to reserve resources and registers the branch transaction with the Transaction Coordinator (TC).
- If the resource reservation is successful, the Transaction Manager (TM) calls commit to commit the global transaction, and the Transaction Coordinator (TC) notifies the Resource Manager (RM) to commit the branch transaction.
- If the resource reservation fails, the Transaction Manager (TM) calls rollback to roll back the global transaction, and the Transaction Coordinator (TC) notifies the Resource Manager (RM) to roll back the branch transaction.
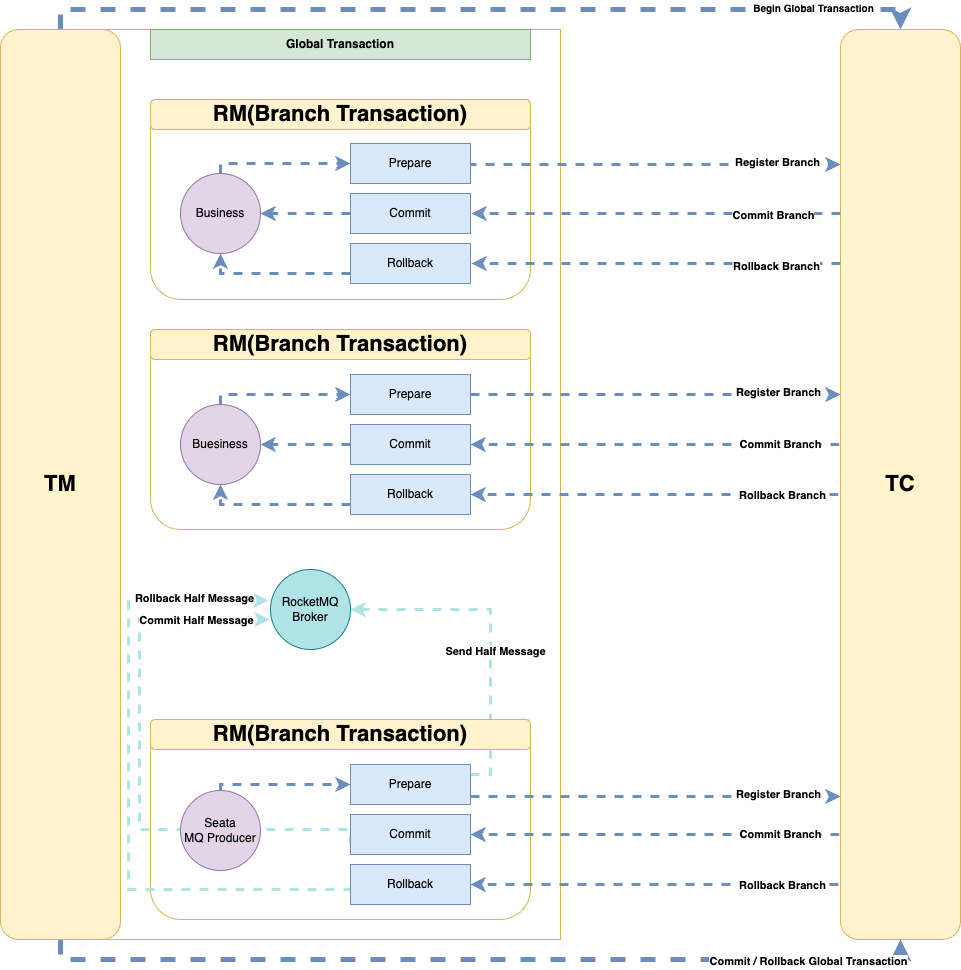
After understanding the overall process of TCC, the above diagram is not difficult to understand. Seata proxies the RocketMQ Producer, automatically converting ordinary messages into RocketMQ transaction messages when the business code needs to send messages, thereby ensuring the consistency of message sending and distributed transactions.
Implementation Principle
public class SeataMQProducerFactory {
public static SeataMQProducer createSingle(String nameServer, String producerGroup) throws MQClientException {
return createSingle(nameServer, null, producerGroup, null);
}
public static SeataMQProducer createSingle(String nameServer, String namespace,
String groupName, RPCHook rpcHook) throws MQClientException {
defaultProducer = new SeataMQProducer(namespace, groupName, rpcHook);
defaultProducer.start();
return defaultProducer;
}
}
From the above code, we can see that SeataMQProducerFactory provides methods to create SeataMQProducer. By calling the createSingle method, we can create a SeataMQProducer instance.
@Override
public SendResult send(Message msg) throws MQClientException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException {
return send(msg, this.getSendMsgTimeout());
}
@Override
public SendResult send(Message msg, long timeout) throws MQClientException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException {
if (RootContext.inGlobalTransaction()) {
if (tccRocketMQ == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("TCCRocketMQ is not initialized");
}
return tccRocketMQ.prepare(msg, timeout);
} else {
return super.send(msg, timeout);
}
}
From the above code, we can see that SeataMQProducer overrides the send method of RocketMQ. By determining whether it is in a global transaction, it decides whether to call the send method of RocketMQ or the prepare method of TccRocketMQ. If the message is sent without participating in a global transaction, it degrades to calling the send method of RocketMQ to send the message.
@LocalTCC
public class TCCRocketMQImpl implements TCCRocketMQ {
@Override
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = SeataMQProducerFactory.ROCKET_TCC_NAME)
public SendResult prepare(Message message, long timeout) throws MQClientException {
BusinessActionContext context = BusinessActionContextUtil.getContext();
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send prepare, xid = {}", context.getXid());
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>(8);
SendResult sendResult = producer.doSendMessageInTransaction(message, timeout, context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
message.setDeliverTimeMs(0);
params.put(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, message);
params.put(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, sendResult);
BusinessActionContextUtil.addContext(params);
return sendResult;
}
@Override
public boolean commit(BusinessActionContext context)
throws UnknownHostException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException, TransactionException {
Message message = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, Message.class);
SendResult sendResult = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, SendResult.class);
if (message == null || sendResult == null) {
throw new TransactionException("TCCRocketMQ commit but cannot find message and sendResult");
}
this.producerImpl.endTransaction(message, sendResult, LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE, null);
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send commit, xid = {}, branchId = {}", context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean rollback(BusinessActionContext context)
throws UnknownHostException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException, TransactionException {
Message message = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, Message.class);
SendResult sendResult = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, SendResult.class);
if (message == null || sendResult == null) {
LOGGER.error("TCCRocketMQ rollback but cannot find message and sendResult");
}
this.producerImpl.endTransaction(message, sendResult, LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE, null);
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send rollback, xid = {}, branchId = {}", context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
return true;
}
}
We can see that TCCRocketMQImpl implements the TCCRocketMQ interface and uses the @LocalTCC and @TwoPhaseBusinessAction annotations, indicating that TCCRocketMQImpl is also a TCC branch transaction, and implements the three scenarios of TCC transactions through the prepare, commit, and rollback methods.
prepare Method
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = SeataMQProducerFactory.ROCKET_TCC_NAME)
public SendResult prepare(Message message, long timeout) throws MQClientException {
BusinessActionContext context = BusinessActionContextUtil.getContext();
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send prepare, xid = {}", context.getXid());
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>(8);
SendResult sendResult = producer.doSendMessageInTransaction(message, timeout, context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
message.setDeliverTimeMs(0);
params.put(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, message);
params.put(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, sendResult);
BusinessActionContextUtil.addContext(params);
return sendResult;
}
In the prepare method, we send a half-transaction message by calling the producer.doSendMessageInTransaction method and save the message and send result to the BusinessActionContext.
commit Method
@Override
public boolean commit(BusinessActionContext context)
throws UnknownHostException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException, TransactionException {
Message message = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, Message.class);
SendResult sendResult = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, SendResult.class);
if (message == null || sendResult == null) {
throw new TransactionException("TCCRocketMQ commit but cannot find message and sendResult");
}
this.producerImpl.endTransaction(message, sendResult, LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE, null);
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send commit, xid = {}, branchId = {}", context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
return true;
}
In the commit method, we commit the transaction message by calling the producerImpl.endTransaction method.
rollback Method
@Override
public boolean rollback(BusinessActionContext context)
throws UnknownHostException, MQBrokerException, RemotingException, InterruptedException, TransactionException {
Message message = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_MSG_KEY, Message.class);
SendResult sendResult = context.getActionContext(ROCKET_SEND_RESULT_KEY, SendResult.class);
if (message == null || sendResult == null) {
LOGGER.error("TCCRocketMQ rollback but cannot find message and sendResult");
}
this.producerImpl.endTransaction(message, sendResult, LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE, null);
LOGGER.info("RocketMQ message send rollback, xid = {}, branchId = {}", context.getXid(), context.getBranchId());
return true;
}
In the rollback method, we roll back the transaction message by calling the producerImpl.endTransaction method.