随着PR https://github.com/apache/incubator-seata/pull/6754 的合并,Seata Server能够做到识别并处理Grpc请求,这意味着任意语言客户端,只需要引入proto文件,就可以和部署在JVM上的Seata Server通信,进而实现分布式事务的全流程。
下面以Go语言为例,向大家演示这一过程。
环境准备
Goland 2024.2
Idea 2024.3
jdk 1.8
go 1.23.3
Seata 2.3.0-SNAPSHOT
libprotoc 3.21.0
操作过程
部署并启动 Seata Server
运行 org.apache.seata.server.ServerApplication#main,如下所示
proto文件导入
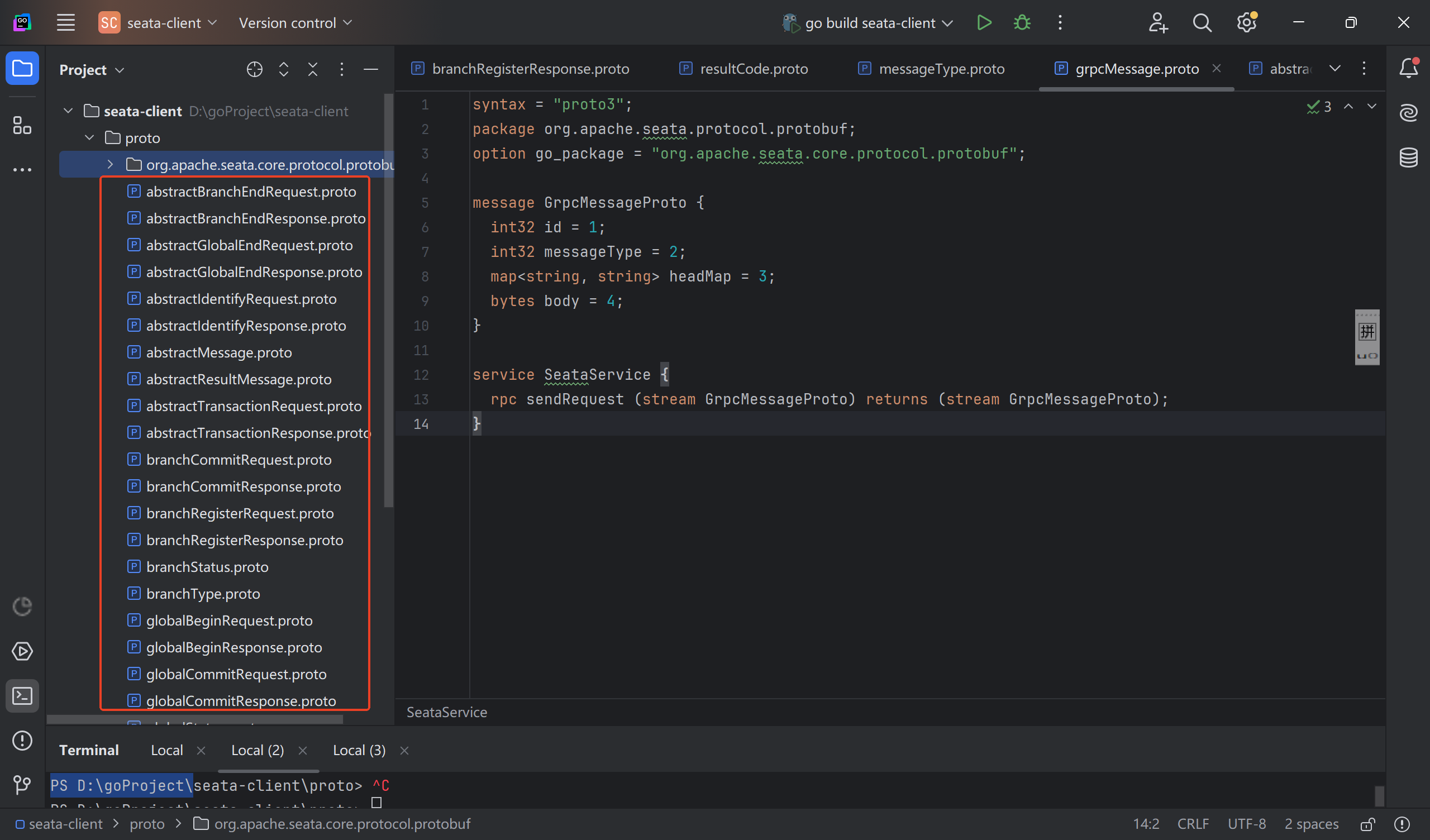
在go项目中导入完成本次事务流程所需的proto文件,包括各类事务请求和响应的proto文件和发起RPC的proto文件。如下所示
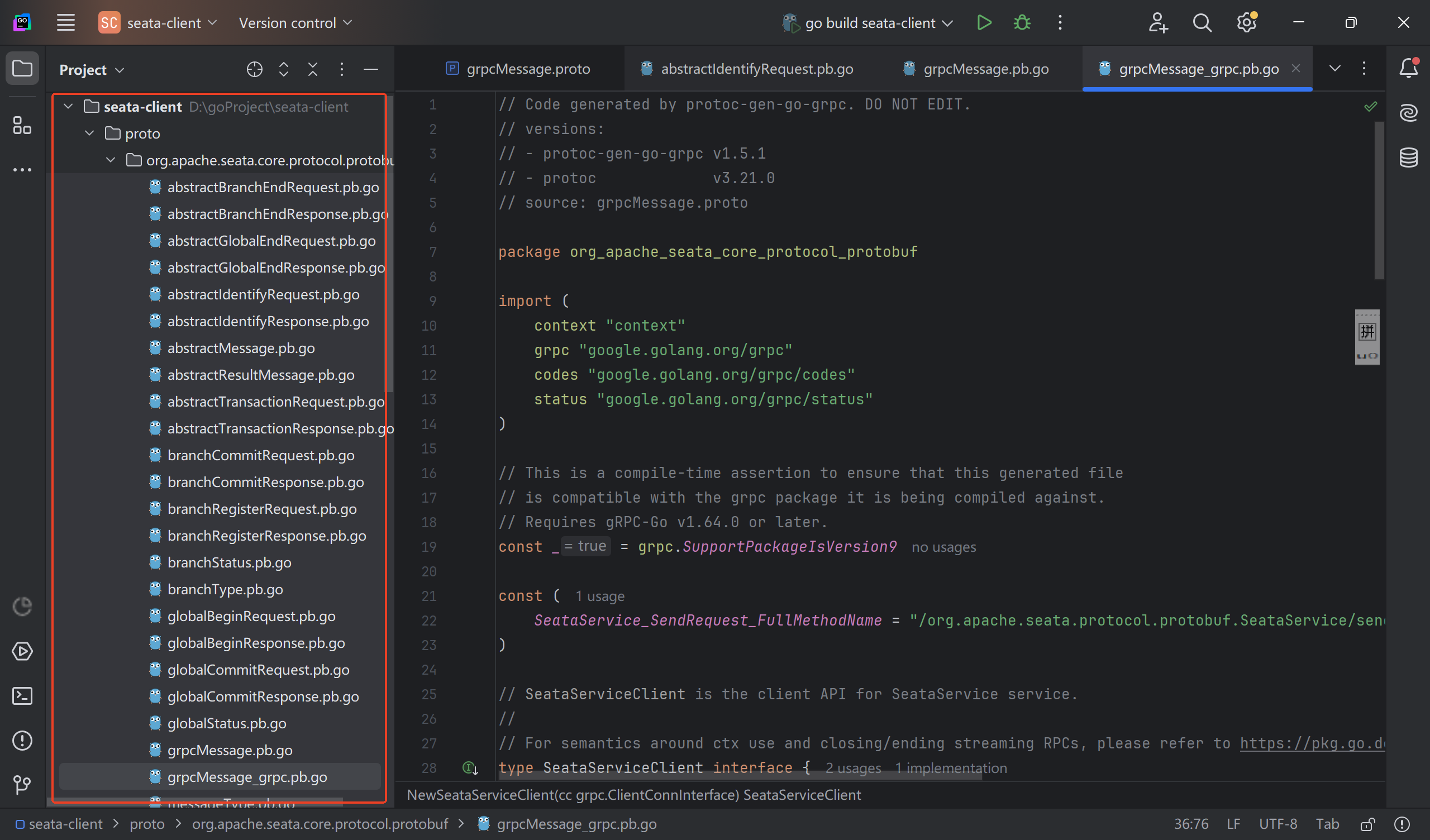
grpc相关文件生成
在上一步导入的proto文件目录下,执行命令
protoc --go_out=. --go-grpc_out=. .\*.proto
执行完后会生成grpc代码,如下所示
grpc调用
在main.go中完成一次分布式事务的流程,并打印Seata Server的响应,代码如下所示
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial(":8091", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := pb.NewSeataServiceClient(conn)
stream, err := client.SendRequest(context.Background())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not sendRequest: %v", err)
}
defer stream.CloseSend()
sendRegisterTm(stream)
xid := sendGlobalBegin(stream)
sendBranchRegister(stream, xid)
sendGlobalCommit(stream, xid)
}
func sendRegisterTm(stream grpc.BidiStreamingClient[pb.GrpcMessageProto, pb.GrpcMessageProto]) {
abstractIdentifyRequestProto := &pb.AbstractIdentifyRequestProto{
ApplicationId: "test-applicationId",
}
registerTMRequestProto := &pb.RegisterTMRequestProto{
AbstractIdentifyRequest: abstractIdentifyRequestProto,
}
registerTMResponseProto := &pb.RegisterTMResponseProto{}
sendMessage(stream, registerTMRequestProto, registerTMResponseProto)
}
func sendGlobalBegin(stream grpc.BidiStreamingClient[pb.GrpcMessageProto, pb.GrpcMessageProto]) string {
globalBeginRequestProto := &pb.GlobalBeginRequestProto{
TransactionName: "test-transactionName",
Timeout: 200,
}
globalBeginResponseProto := &pb.GlobalBeginResponseProto{}
sendMessage(stream, globalBeginRequestProto, globalBeginResponseProto)
return globalBeginResponseProto.Xid
}
func sendBranchRegister(stream grpc.BidiStreamingClient[pb.GrpcMessageProto, pb.GrpcMessageProto], xid string) {
branchRegisterRequestProto := &pb.BranchRegisterRequestProto{
Xid: xid,
LockKey: "1",
ResourceId: "test-resourceId",
BranchType: pb.BranchTypeProto_AT,
ApplicationData: "{\"mock\":\"mock\"}",
}
branchRegisterResponseProto := &pb.BranchRegisterResponseProto{}
sendMessage(stream, branchRegisterRequestProto, branchRegisterResponseProto)
}
func sendGlobalCommit(stream grpc.BidiStreamingClient[pb.GrpcMessageProto, pb.GrpcMessageProto], xid string) {
abstractGlobalEndRequestProto := &pb.AbstractGlobalEndRequestProto{
Xid: xid,
}
globalCommitRequestProto := &pb.GlobalCommitRequestProto{
AbstractGlobalEndRequest: abstractGlobalEndRequestProto,
}
globalCommitResponseProto := &pb.GlobalCommitResponseProto{}
sendMessage(stream, globalCommitRequestProto, globalCommitResponseProto)
}
func sendMessage(stream grpc.BidiStreamingClient[pb.GrpcMessageProto, pb.GrpcMessageProto], req proto.Message, response proto.Message) {
anyMsg, err := anypb.New(req)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not new any msg: %v", err)
}
marshal, err := proto.Marshal(anyMsg)
msg := &pb.GrpcMessageProto{
HeadMap: map[string]string{},
Body: marshal,
}
err = stream.Send(msg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not send msg: %v", err)
}
resp, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to receive message: %v", err)
}
body := resp.Body
var anyMessage anypb.Any
err = proto.Unmarshal(body, &anyMessage)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to unmarshal to any: %v", err)
}
err = anypb.UnmarshalTo(&anyMessage, response, proto.UnmarshalOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to unmarshal to message: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Received: %+v", response)
}
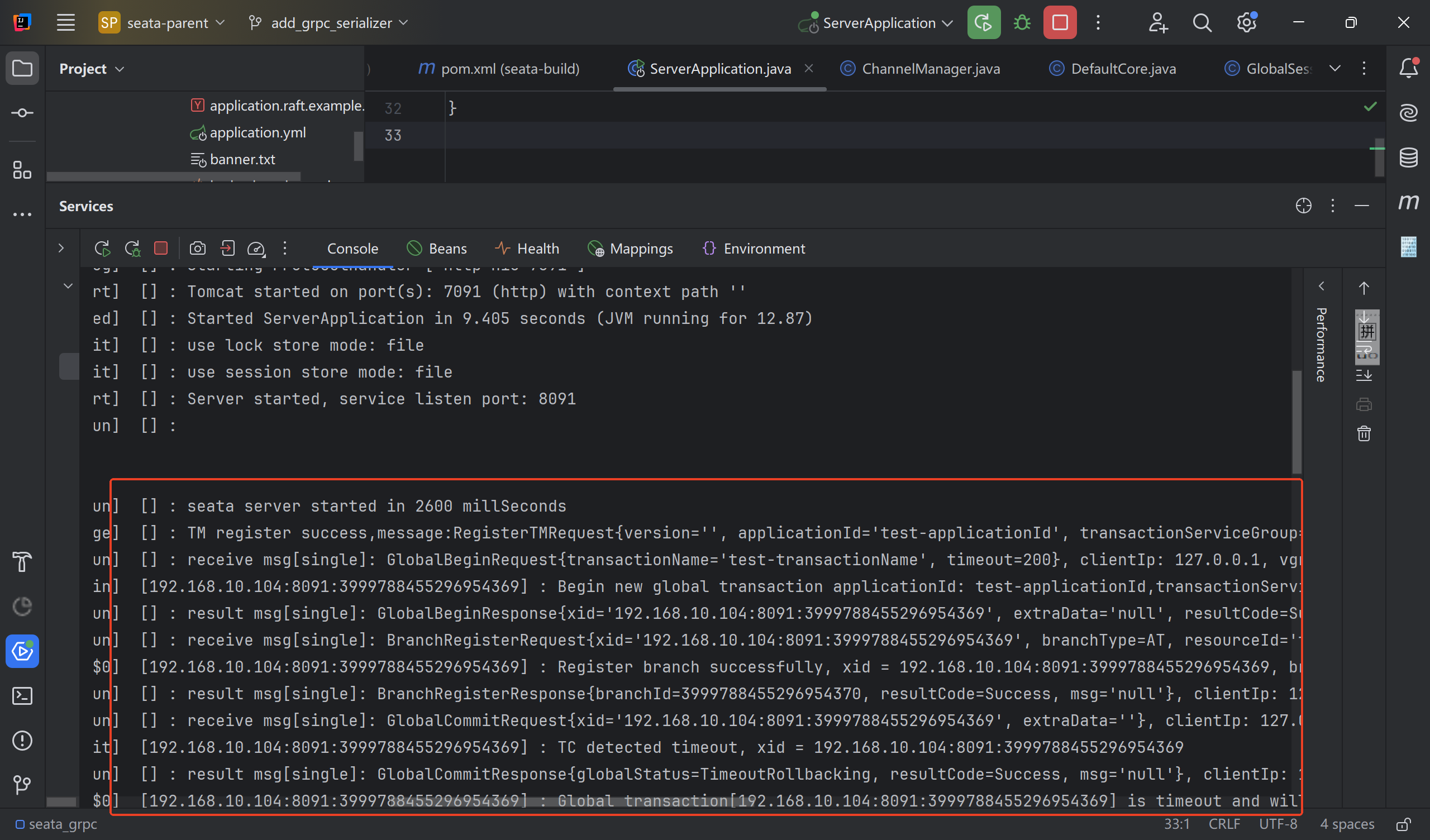
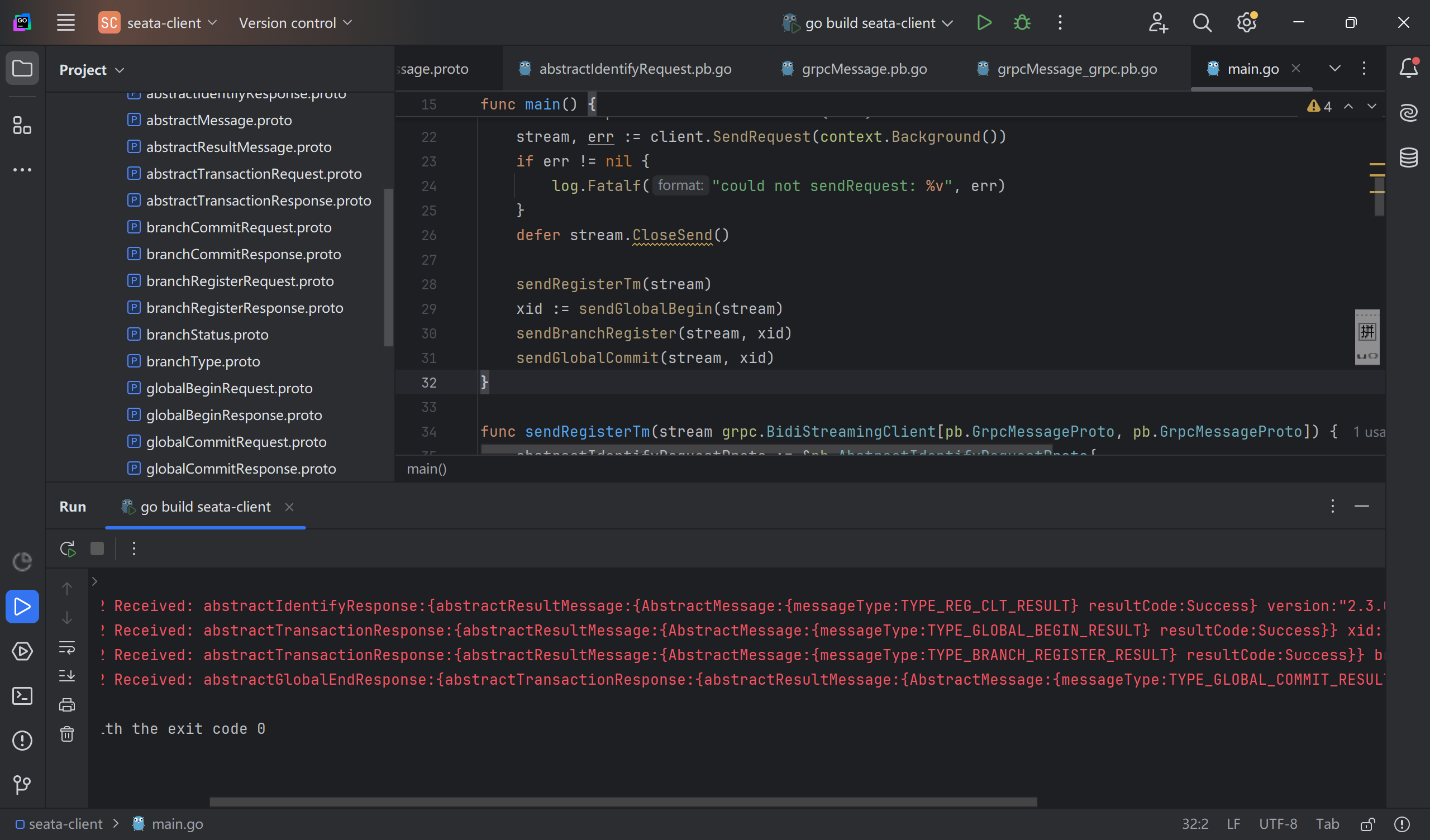
运行后,Seata Server控制台打印如下
Go客户端控制台打印如下
实现原理
proto设计
为了实现与多语言grpc客户端的通信,Seata Server定义了grpcMessage.proto,其中定义了装配 Seata各种Message对象的GrpcMessageProto和装配Seata各类通信请求的双向流接口sendRequest。Seata Server以grpcMessage.proto作为媒介,可以实现与多语言客户端的通信
syntax = "proto3";
package org.apache.seata.protocol.protobuf;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_outer_classname = "GrpcMessage";
option java_package = "org.apache.seata.core.protocol.generated";
message GrpcMessageProto {
int32 id = 1;
int32 messageType = 2;
map<string, string> headMap = 3;
google.protobuf.Any body = 4;
}
service SeataService {
rpc sendRequest (stream GrpcMessageProto) returns (stream GrpcMessageProto);
}
除此之外,还定义了GrpcSerializer,适配 Seata 的序列化器SPI体系,用于实现protobuf字节流和Seata消息对象的互相转换
grpc协议识别
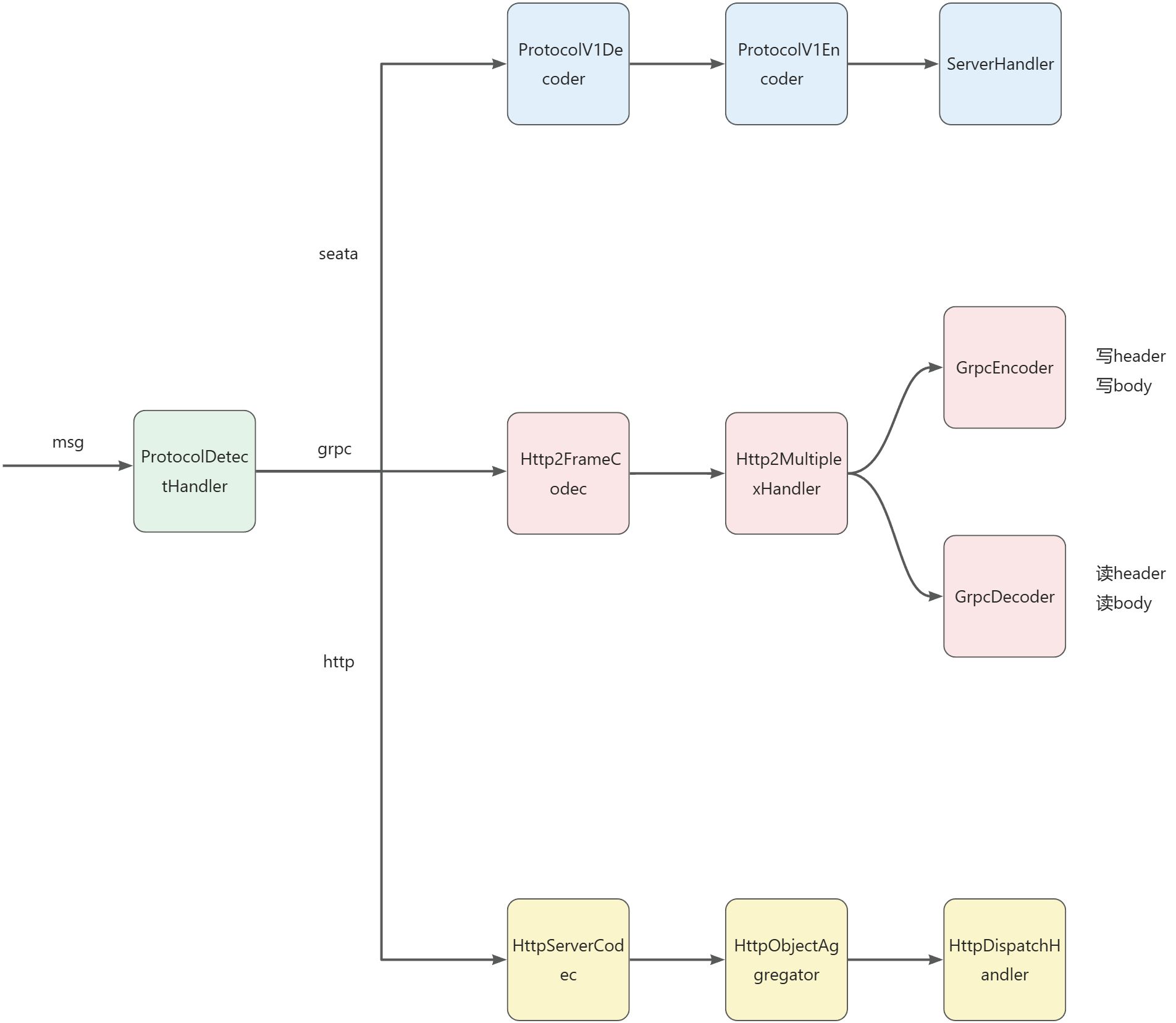
Seata Server实现了ProtocolDetectHandler和ProtocolDetector。ProtocolDetectHandler作为ByteToMessageDecoder,在收到消息时,会遍历ProtocolDetector列表寻找能够识别当前消息的ProtocolDetector,ProtocolDetector通过识别魔数的方式区分Seata协议,Http1.1协议,Http2协议,一旦识别成功,会将能够处理该协议的ChannelHandler加入到当前Channel的Pipeline中
grpc请求发送与处理
Seata Server 实现了GrpcEncoder和GrpcDecoder,GrpcEncoder负责将Seata的RpcMessage转换为grpc原生客户端可识别的GrpcMessageProto,并在header中填充status,contentType等协议头用于与grpc原生客户端通信。GrpcEncoder还负责适配grpc协议规范,将压缩位、长度、消息体按照grpc协议约定的顺序写入channel
GrpcDecoder负责处理grpc原生客户端的请求。由于grpc客户端在底层传输时通过队列的方式实现了请求的分批flush,因此GrpcDecoder还负责将一批请求进行拆包。最终GrpcDecoder将protobuf字节流转换为一个或多个RpcMessage,并传递给Seata请求处理器
grpc连接的建立和管理
Server端只需配置配置一个ProtocolDetectHandler,即可完成各种类型连接的识别和建立
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ProtocolDetector[] defaultProtocolDetectors = {
new Http2Detector(getChannelHandlers()),
new SeataDetector(getChannelHandlers()),
new HttpDetector()
};
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(nettyServerConfig.getChannelMaxReadIdleSeconds(), 0, 0))
.addLast(new ProtocolDetectHandler(defaultProtocolDetectors));
}
Client端在每次获取Channel时,如果当前配置的通信方式是Grpc,则会以NioSocketChannel作为父Channel,获取一个Http2MultiStreamChannel,并在该Channel中添加grpc相关的handler
if (nettyClientConfig.getProtocol().equals(Protocol.GPRC.value)) {
Http2StreamChannelBootstrap bootstrap = new Http2StreamChannelBootstrap(channel);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channel.pipeline().addLast(new GrpcDecoder());
channel.pipeline().addLast(new GrpcEncoder());
if (channelHandlers != null) {
addChannelPipelineLast(channel, channelHandlers);
}
}
});
channel = bootstrap.open().get();
}